Overview of Income Tax Returns in India for FY 2023-24
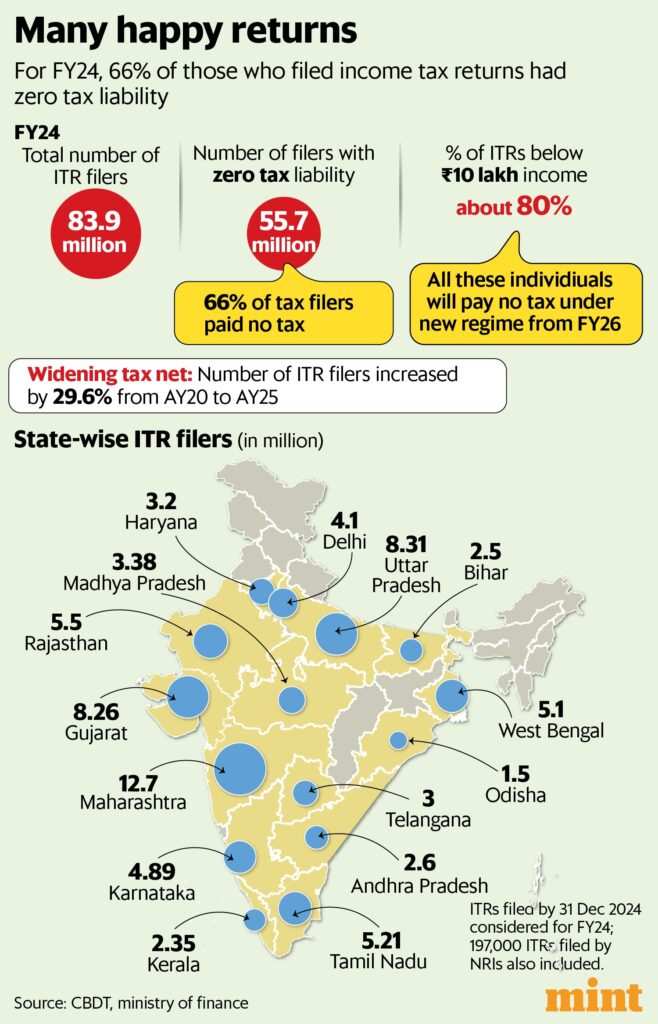
As of December 2024, around 83.9 million Indians have filed their Income Tax Returns (ITRs) for the financial year 2023-24. Among these, only 28.2 million, which is roughly 34%, actually paid taxes. This leaves 55.7 million, or 66%, of filers with no tax liability at all. These figures were released by the finance ministry during the ongoing Lok Sabha session, shedding light on the current state of tax filings in India.
Changes in Tax Rebate Limits
In the recent Budget 2025, the government announced an increase in the tax rebate limit under the new income tax regime. Starting from the financial year 2025-26, the limit will rise to ₹12 lakh (or ₹12.75 lakh for salaried employees). This means that individuals earning less than this amount will effectively not have to pay any income tax.
Expected Trends for Future Tax Filers
If past trends continue, it is anticipated that around 80% of individuals filing ITRs for the financial year 2025-26 will report zero tax liability. This is based on current patterns observed among taxpayers.
Understanding Taxpayer Data
Data from the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) reveals that for the assessment year 2023-24, about 83.6% of the 79.7 million taxpayers reported a taxable income of ₹10 lakh or less. Given the increase in the tax rebate, most of these individuals will not owe any tax unless their taxable income increases significantly—by at least 20%—to surpass the ₹12 lakh threshold starting in FY 2026.
Filing Timeline for ITRs
It’s essential to know that ITRs are filed in the year following the respective financial year. For instance, when we talk about the financial year 2024-25, the corresponding tax returns will be filed in the assessment year 2025-26.
States with the Most ITR Filers
When we look at regional data, Maharashtra stands out as the state with the highest number of tax filers. In the assessment year 2025, approximately 12.7 million ITRs were submitted from Maharashtra. Following Maharashtra are Uttar Pradesh and Gujarat, with 8.31 million and 8.26 million filers, respectively. Among southern states, Tamil Nadu recorded about 5.21 million ITRs filed.
Growth in Tax Filing
Over the last five years, there has been a notable increase in the number of individuals filing ITRs. Comparing assessment year 2020 (AY20) to assessment year 2025 (AY25), the number of filers has risen by about 29.6%. One driving factor for this growth could be the introduction of tax rebate limits in both tax regimes during recent years.
- Individuals earning up to ₹5 lakh have been eligible for a tax rebate under the old regime.
- The rebate limit under the new regime has now been set at ₹7 lakh, which will further increase to ₹12 lakh from FY26.
Importance of Filing ITRs
It’s essential to understand that just because individuals earn below the rebate limit, it does not mean they are exempt from filing income tax returns. They are still required to file ITRs to demonstrate that while their income may surpass the basic exemption limit, they are still eligible for a rebate and thus do not pay taxes.
Encouragement for Compliance among Small Businesses
According to an income tax officer who chose to remain unnamed, the increased rebate policy has encouraged small businesses that previously avoided filing ITRs to officially submit their returns without the pressure of tax payments. This policy underpins why such a large percentage of tax filers—around two-thirds—end up with no tax obligation.
Conclusion
In summary, the current landscape of income tax filings in India reflects significant trends toward minimal tax liability for a large portion of filers. The recent increases in tax rebate limits are expected to further this trend, creating an environment that promotes greater compliance among taxpayers, particularly small businesses. With more individuals participating in the tax system, the government’s strategy appears to be fostering a more robust and transparent economy. Understanding these dynamics is essential for all taxpayers as they navigate their financial responsibilities.